Photo ID
From driver’s licenses to student membership cards to national ID schemes, cards are the most widely used method for verifying age, identity and the associated access to rights and benefits in society. Verification can take the form of a simple photograph or signature, or for more secure applications, can be stored in an electronic chip on the card in the form of a biometric such as a fingerprint or a password, such as a PIN. Cards can be secured to prevent forgeries by using electronic keys contained in the chip or by physical visual methods such as UV printing, holograms, micro text or HoloKote watermark.
Physical Access
Cards, and most commonly smart cards – with an embedded electronic chip, are increasingly accepted as the credential of choice for securely controlling physical access. Smart cards are used to authenticate individuals, to determine the appropriate level of access, and physically admit the cardholder to a facility, most commonly using a card reader at the point of entry. Multiple access applications can be contained on a smart card, granting users access to both physical and logical resources without the need for multiple credentials. Access rights can be changed dynamically or revoked, depending on perceived threat level or if the system is in any way compromised.
Payments
Plastic cards have become the global standard for electronically purchasing goods and services. In the last 20 years insecure magnetic stripe and embossed numbering systems have been replaced by a secure electronic system of data and keys held on the card’s embedded chip. This standard was established and has been championed by EMV (Europay, Mastercard, Visa). These secure cards can be issued locally, for example in branch at the point of account opening, using desktop card printers fitted with the appropriate EMV encoding devices.
Logical Access
In today’s digital and connected World, securing electronic data and networks is as important as securing access to physical assets such as building and facilities. Password-based access is now widely acknowledged to be a significant security risk and many organisations, across all industries, are using multi-factor authentication to grant access to data. Multi-factor can be a combination of something you know (i.e. a password) with something you have (an authenticated smart card) and something you are (a biometric such as fingerprint). Cards can support all of these authentication methods, with all factors contained on the chip of a single card, enabling flexible, secure and private access to data and networks.
Time and attendance
Time and attendance systems are used to record when employees start and stop work, and often the department where the work is undertaken. Tracking of breaks, lunch-breaks, vacation time and sickness absence is also commonplace. Traditional paper-based or password-based tracking systems which are open to compromise are being replaced by electronic systems, often using cards containing electronic data. Multi-application smart cards that are used to grant access to physical and logical resources can also be used to track attendance using a range of technologies from a basic (but insecure) magnetic stripe to Ultra High Frequency proximity systems that track employees’ whereabouts whenever they are within the building.
Loyalty and membership
Cards as a token of membership of a club, association or loyalty scheme are common place. Introducing a smart card element to these can open up a range of other applications including access to facilities, payment in members-only facilities such as restaurants, bars or vending machines, and the online booking of club resources. Loyalty cards, pioneered by large supermarket groups and gas stations are now adopted by many smaller retail outlets, often using desktop ID card printers to instantly issue personalised cards to customers.
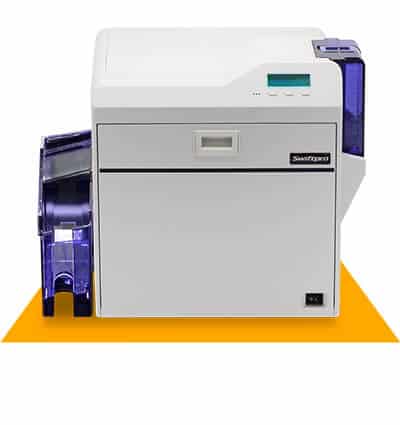
See our range of ID Card printers or get in touch here or call us at (042) 35341901.









Leave A Comment